Corneal Transplantation
Cornea Definition: What is its Role in the Eye?
The cornea is the eye’s transparent front layer and plays a crucial role in the vision process. Serving as a protective barrier for the eye, it significantly contributes to focusing light onto the retina. The cornea is both rigid and elastic, allowing it to maintain the eye’s shape. It is also densely innervated, making it one of the most sensitive parts of the eye. Notably, the cornea lacks blood vessels and receives oxygen and nutrients from tears and the aqueous humor that fills the eye’s anterior chamber. The cornea also acts as a lens, aiding in gathering light and directing it towards the eye’s lens, which then focuses the image onto the retina.
Keratoconus and Its Impact: How Does It Affect Vision?
Keratoconus is a degenerative condition that alters the shape and structure of the cornea, causing it to thin and protrude outward in a conical shape. This alteration significantly distorts vision. Typically emerging in adolescence or early twenties, it progresses gradually. Keratoconus disrupts the correct focusing of light onto the retina, resulting in blurred and double vision, difficulty in night vision, and light sensitivity. In advanced cases, special contact lenses or corneal surgery may be necessary to enhance vision.
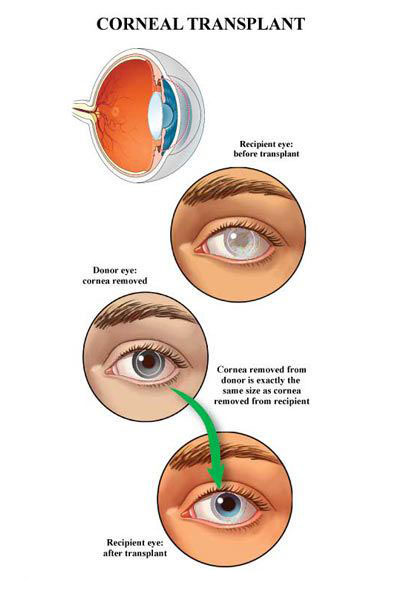
Corneal transplantation becomes necessary when the cornea is irreparably damaged and cannot be treated by conventional methods. Common reasons for corneal transplantation include corneal damage due to injuries or infections, structural changes like in keratoconus, and diseases affecting corneal transparency such as corneal degeneration. Transplantation is also considered when other treatments fail or the cornea is so severely damaged that it cannot effectively perform its functions.
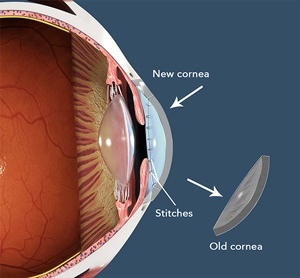
Corneal transplantation is categorized into several types based on the case’s needs. The first type is full corneal transplantation, where the entire cornea is replaced with one from a donor. The second type is partial transplantation, involving the replacement of only specific corneal layers. Partial transplantation offers advantages such as a shorter recovery period and a lower risk of rejection. The type of transplantation is chosen based on several factors, including the cornea’s condition and underlying diseases.
Preparing for corneal transplantation involves several steps, starting with a comprehensive eye health assessment. This assessment is conducted to determine the extent of corneal damage and whether transplantation is the best option. The assessment includes detailed corneal examinations and vision tests. Additionally, the doctor discusses with the patient the expectations and potential risks of the procedure, and the patient is required to undergo blood tests and refrain from taking certain medications that might affect the surgery.
The success of corneal transplantation is measured by several criteria, such as improved vision, healing without complications, and the absence of rejection of the transplanted cornea. Success rates depend on various factors, including the health of the recipient cornea, the surgeon’s skill, and the post-operative care followed. Vision can significantly improve after transplantation, but some challenges such as the need for glasses or lenses for vision correction may arise.
Risks and Complications of Corneal Transplantation:
Like any surgical procedure, corneal transplantation carries its risks and complications. Common complications include infection, swelling, increased pressure inside the eye (glaucoma), and cataract formation. Complications related to stitches and scarring can also occur, and in some cases, the body’s rejection of the transplanted cornea can lead to the failure of the transplantation. Managing these risks requires careful monitoring after the procedure and strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions, including the use of prescribed medications such as anti-inflammatory drops and antibiotics.
Signs of the Body's Rejection of the Transplanted Cornea:
Rejection of the transplanted cornea is one of the serious complications of corneal transplantation. Early symptoms of rejection include redness and pain in the eye, changes in vision such as blurriness or decreased clarity, and light sensitivity. It is very important to pay attention to these symptoms and contact the doctor immediately upon their appearance. Early detection and prompt treatment of rejection, which may include strong steroid drops or other immunotherapies, can increase the chances of success of the transplanted cornea.
Duration of Corneal Transplantation Procedure:
The corneal transplantation procedure typically takes less than an hour and is performed under local anesthesia, allowing the patient to return home on the same day. However, a rest period should be planned after the procedure, and regular follow-ups with the doctor are necessary to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the transplantation.
Expectations for Vision Improvement After Corneal Transplantation
The improvement in vision after corneal transplantation varies from patient to patient. Some patients begin to notice an improvement in vision within a few weeks after the procedure, while others may need several months to achieve full vision stabilization. The improvement also depends on the type of transplantation and the individual’s response to healing. Regular follow-ups with the doctor are necessary to assess the progress of healing and adjust any visual corrections if necessary.
Guidelines and Tips After Corneal Transplantation
Eye care after corneal transplantation is extremely important. This includes using prescribed eye drops, protecting the eye from injuries, dust, and intense light. It is advised to avoid rubbing the eye and activities that may increase the risk of injury. It is also important to maintain hand cleanliness to avoid infection and to keep medical follow-up appointments to monitor healing progress.
Working Hours
Saturday
7 pm to 9 pm
Sunday
7 pm to 9 pm
Monday
7 pm to 9 pm
Tuesday
7 pm to 9 pm
Wednesday
7 pm to 9 pm
Thursday
Closed
Friday
Closed
Ramadan Working Hours
Saturday to Wednesday from 9 pm to 11 pm
Location
21st Ismail Ramzy st. – El-Bostan – Heliopolis – 4th floor
01110114354
01222422637
0226331026
(7 pm to 9 pm)
Make Appointment
Always happy to receive your inquiries
